Address
1, Jln Taylors, 47500 Subang Jaya, Selangor, Malaysia
Batch 21
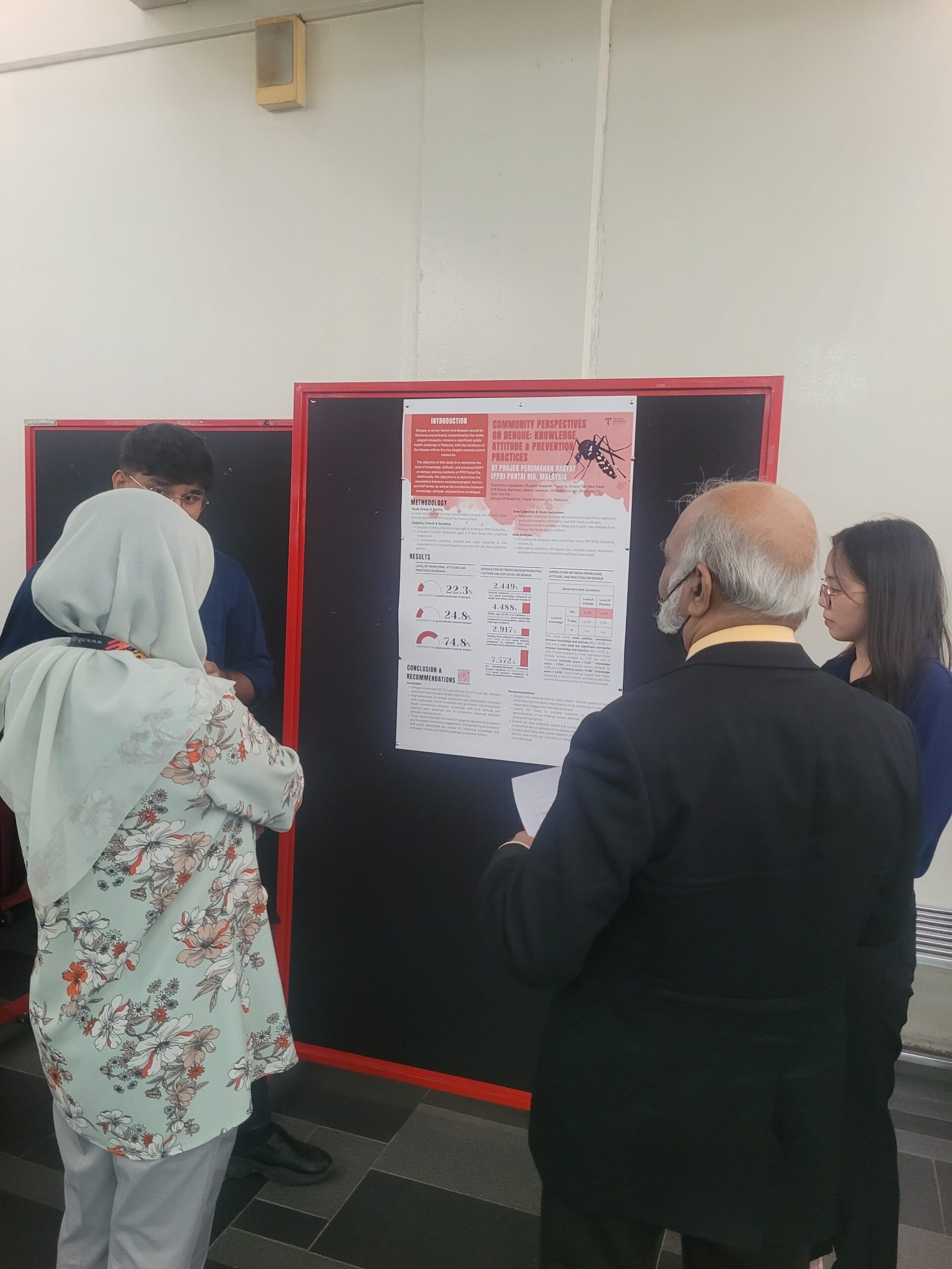
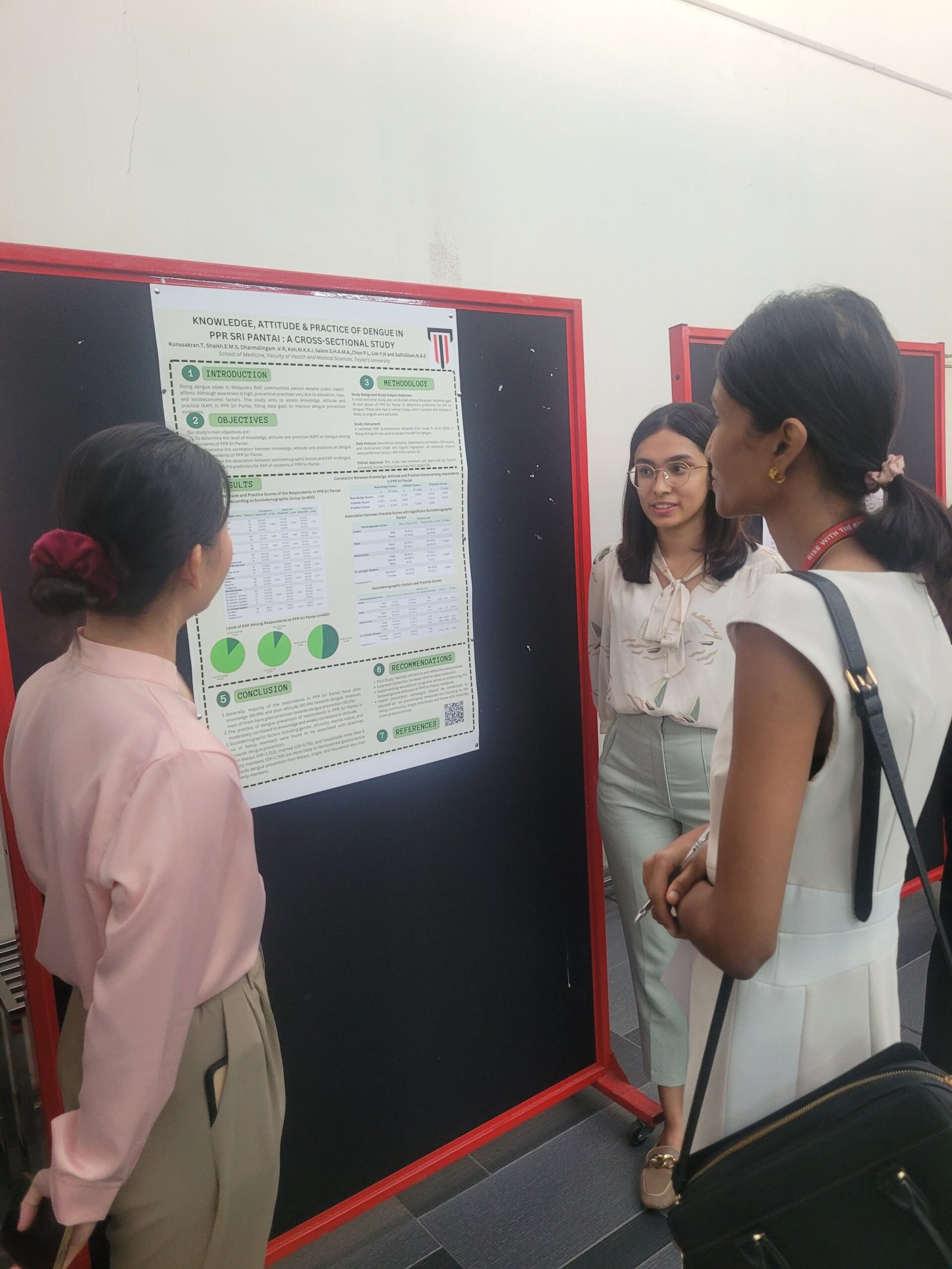
1. Knowledge, Attitude & Practice of Dengue in PPR Sri Pantai: A Cross-Sectional Study
This study examined the knowledge, attitude, and practice (KAP) regarding dengue prevention in PPR Sri Pantai. The results revealed that most respondents had poor knowledge (86.9%) and poor attitudes (90.4%) toward dengue, yet over half practiced good dengue prevention strategies (52.3%). The study highlighted that marital status, ethnicity, and household size significantly influenced preventive practices, emphasizing the need for targeted health education campaigns.
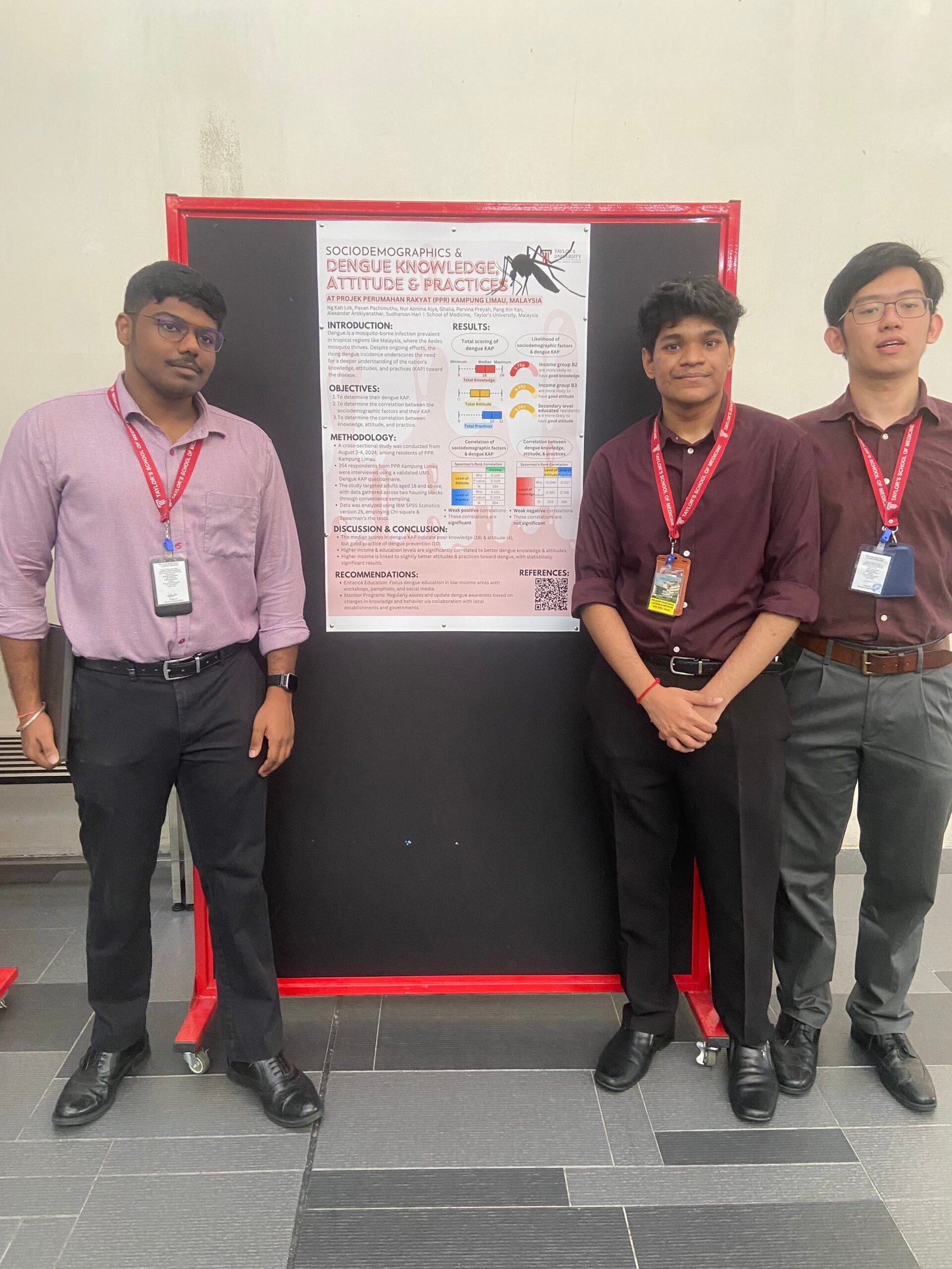
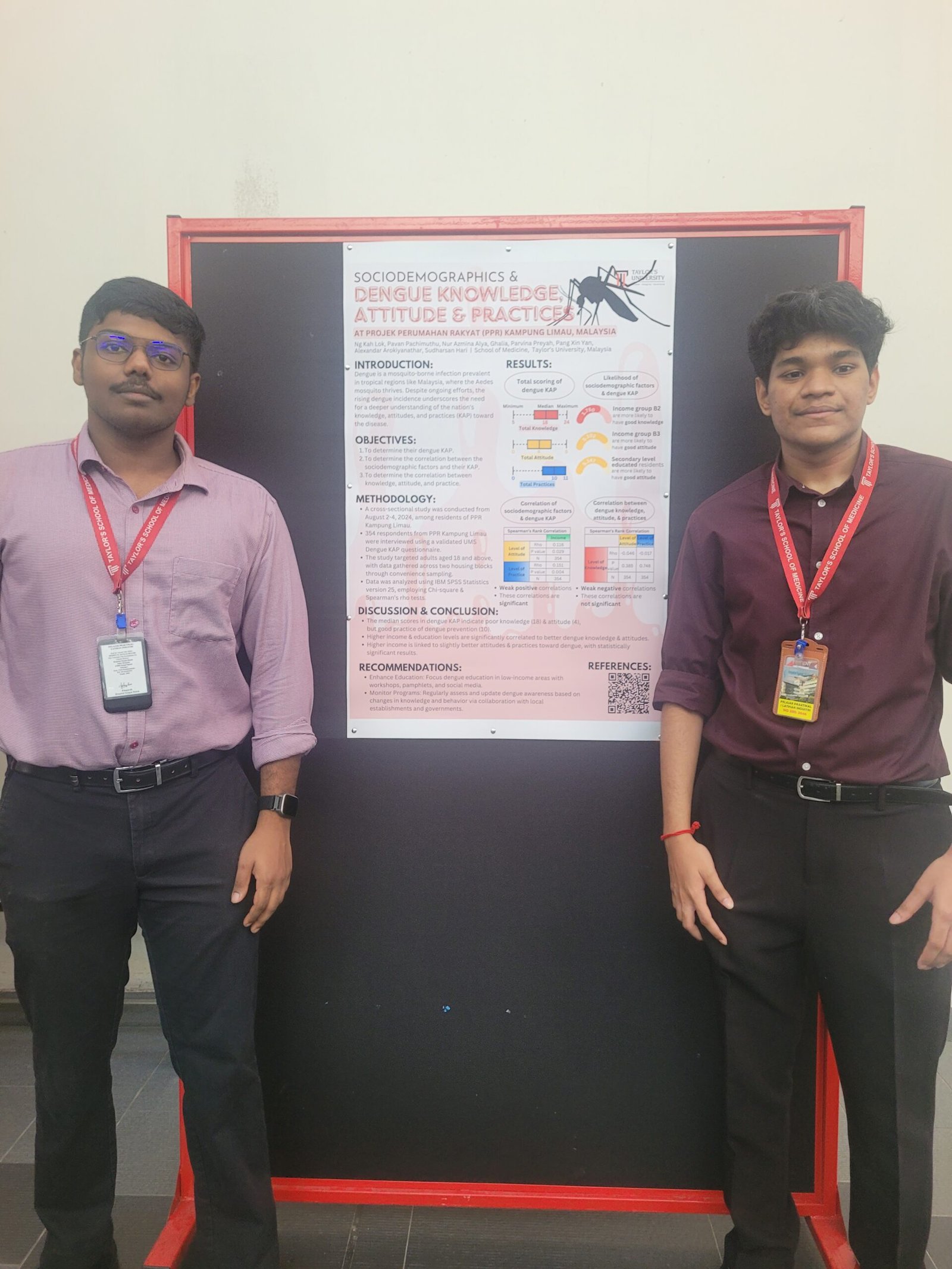
2. Knowledge, Attitude & Practice of Dengue in PPR Kampung Limau, Malaysia
This study explored dengue-related knowledge, attitudes, and preventive practices in PPR Kampung Limau. Findings showed that dengue knowledge and attitudes were generally poor, while preventive practices were relatively better. Higher income and education levels were linked to improved dengue prevention behaviors. The study recommends educational interventions targeting low-income households to enhance awareness and preventive measures.
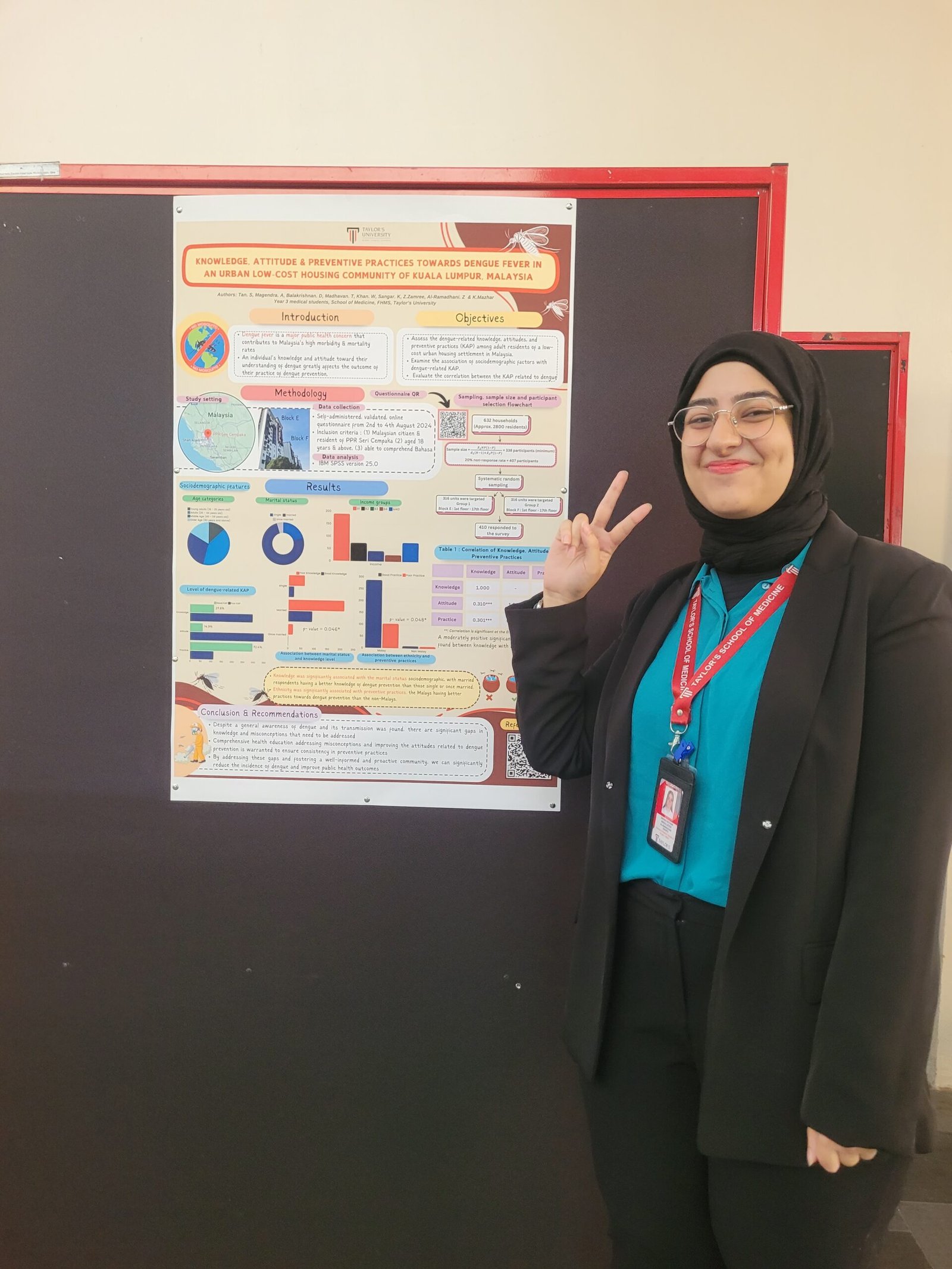
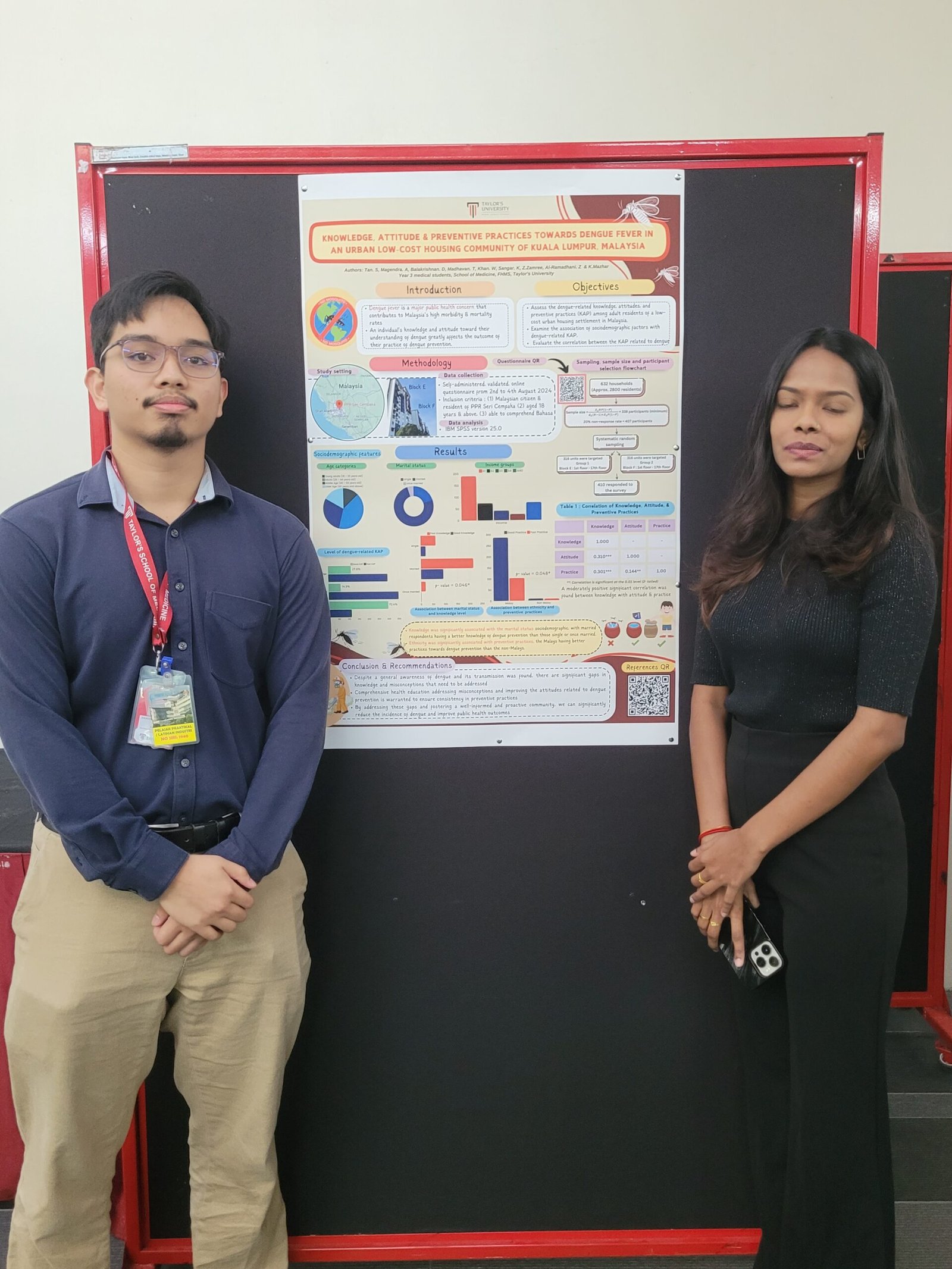
3. Assessment of Knowledge, Attitude & Preventive Practices Toward Dengue Fever in an Urban Low-Cost Housing Community
This research assessed dengue prevention behaviors in an urban low-income setting. While awareness of dengue symptoms was high, significant misconceptions about transmission and prevention persisted. The study emphasized the need for focused educational programs to correct misinformation and promote effective preventive practices.







































Batch 20
1. Assessment of Level of Knowledge and Perception on Diabetes Mellitus in PPR Sri Pantai, Kuala Lumpur
This study assessed diabetes knowledge and perception among residents of PPR Sri Pantai. It found that a significant portion of both diabetic and non-diabetic participants had moderate to low knowledge about diabetes, with education level and total household income influencing knowledge scores. The study emphasizes the need for community outreach programs to improve diabetes awareness.
2. Prevalence of Depression and Its Association with Food Security and Sociodemographic Factors Among Adult Residents of a Low-Income Urban Settlement in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
This study explored the prevalence of depression and its relationship with food security in a low-income community. It found that race and food insecurity were significant predictors of depression, with financial constraints contributing to poor mental health outcomes. The study highlights the importance of public health initiatives addressing food security and mental well-being.
3. Assessing Nicotine Dependence Using eFTND, PSECDI & EASI Questionnaires Among E-Cigarettes Users in an Urban Public Housing Scheme
This study compared different questionnaires for measuring nicotine dependence among e-cigarette users. It found that the PSECDI questionnaire is a reliable alternative to the widely used eFTND. Additionally, dual users (e-cigarette + traditional cigarettes) showed significantly higher nicotine dependence compared to sole e-cigarette users. The study suggests targeted interventions for smoking cessation.
4. Food Security and Dietary Patterns in Communities Living in People’s Housing Project Seri Pantai, Kuala Lumpur
This research examined food security and its impact on meal patterns, food consumption, and mental health in a low-income community. It found that lower-income households were more likely to experience food insecurity, affecting their diet quality. Additionally, food-insecure individuals were more likely to suffer from depression, underscoring the need for nutrition education and financial assistance programs.
5. Prevalence and Associated Factors of Sleep Quality Among Adults in PPR Sri Pantai, Kuala Lumpur
This study investigated sleep quality and its association with sociodemographic factors, vaping habits, and mental health. It found that vaping, depression, and lower education levels were significant predictors of poor sleep quality. The study suggests public health interventions to improve sleep hygiene and mental health awareness.






































Batch 19
1. Physical Activity Status of Adult E-Cigarette Users in a Suburban Public Housing Area and Its Vicinity in the Federal Territory of Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
This study examined the physical activity levels among e-cigarette users in a suburban public housing area. The findings showed that e-cigarette users were less likely to engage in moderate-to-vigorous physical activity and had a higher risk of mental health issues. The study suggests interventions to improve physical activity and mental health among e-cigarette users.
2. Quality of Life in Low-Income Households Among Residents Living in Perumahan Awam Sri Johor, Cheras in 2023
This research assessed quality of life (QoL) across four domains: physical health, psychological health, environment, and social relationships. The psychological domain had the highest mean score, while environmental factors were rated the lowest. A significant correlation was found between smoking status, income levels, and QoL.
3. Vapers’ Mental Health
This study investigated the association between e-cigarette use and mental health disorders (MHD), specifically depression and anxiety. The results indicated that young, highly stressed individuals were more likely to develop MHD, and those unsure about their nicotine intake were more likely to experience anxiety. However, nicotine dependence itself showed no significant correlation with MHD.
4. Association Between Electronic Cigarette Use and Sleep Quality in an Urban Public Housing Area
This study examined how vaping affects sleep quality among e-cigarette users. The findings showed that female users, those with strong behavioral dependence on vaping, and individuals with no or low nicotine dependence were more likely to experience poor sleep quality. Dual users (those who use both e-cigarettes and traditional cigarettes) had better sleep quality compared to sole e-cigarette users.
5. Association Between Eating Habits and Body Mass Index Among Children and Adolescents in an Urban Poor Community
This study explored the relationship between dietary habits and BMI in children and adolescents from a low-income community. The findings revealed that snack consumption was significantly associated with being underweight, while breakfast consumption had no statistical impact on BMI. Household income also played a role in nutritional status.
6. Prevalence and Predictors of Depression Among the Elderly in a Primary Health Care Setting in Selangor, Malaysia
This study assessed depression among the elderly and identified smoking status, chronic illnesses, and social support levels as significant risk factors. The results emphasize the importance of early mental health screening and interventions in primary care settings to improve elderly well-being.
7. Assessment of Help-Seeking Behavior for Mental Health in Urban Primary Care Clinics</strong>
This study investigated how individuals seek help for mental health issues. The results showed that family and friends remained the preferred sources of support, while a significant portion of participants did not seek any help at all. The study highlights the need for greater mental health awareness and accessibility to professional support.
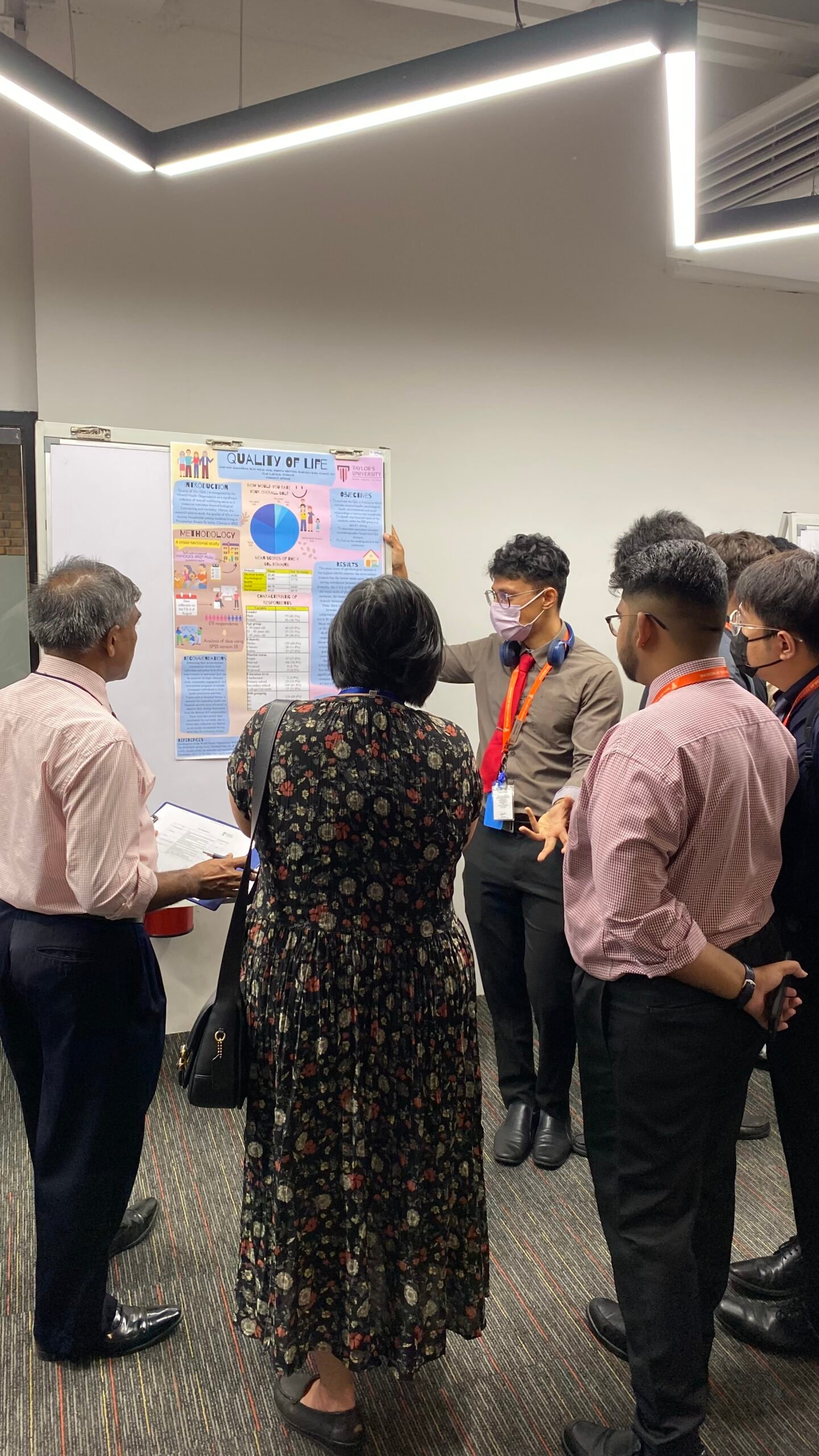








































Batch 18
1. Prevalence and Predictors of Life Satisfaction Among Adolescent and Adult Community Living in Selangor, Malaysia: A Cross-Sectional Study
This study explored factors affecting life satisfaction in Selangor. It found that marital status, chronic illness, and happiness levels were significant predictors, while other sociodemographic factors showed minimal impact.
2. Assessment of Level of Knowledge and Awareness About Diabetes Mellitus Among Individuals Who Visited Primary Healthcare Centres in Selangor, Malaysia
This study assessed diabetes awareness among primary care patients. While general knowledge was moderate, those with higher income levels had better awareness. The study highlights the need for educational programs targeting lower-income groups.
3. Depression and Its Associated Factors Among the Elderly in a Primary Health Care Setting in Selangor, Malaysia: A Cross-Sectional Study
This study analyzed the prevalence of obesity and its associated risk factors, including lifestyle habits, diet, and socioeconomic influences, among adults in a low-income urban community.
4. Assessment of Help-Seeking Tendency Among Patients Attended to Clinics in the Urban Area
This study investigated help-seeking behavior for mental health issues, revealing that family and friends were preferred sources of support over professional help. A large proportion of participants avoided seeking help, pointing to mental health stigma and accessibility issues.
5. Obesogenic Factors Among Malaysian Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study
This study examined obesity-related risk factors such as diet, socioeconomic status, and lifestyle. The findings showed that age was the most significant predictor of obesity, with older individuals having higher odds of being overweight or obese.
6. Sociodemographic and Lifestyle Predictors of Mental Health of Adult Population in Selangor
This research examined depression, anxiety, and stress (DAS) prevalence in adults. Employment status, alcohol consumption, and sleep duration were major influencing factors, highlighting the importance of mental health awareness and workplace interventions.
7. Prevalence & Predictors of Happiness and Life Satisfaction Among Adults in Primary Care Clinics in Selangor, Malaysia
This study assessed happiness and life satisfaction levels in a primary care setting. Physical activity, chronic illness, and smoking habits significantly impacted life satisfaction, emphasizing the role of healthy lifestyle choices.































Batch 17
1. Obesogenic Factors Among Malaysian Adults
This cross-sectional study explored the association between obesity and factors like fast food consumption, sugary snacks, socioeconomic status, and quality of life. The study found that age was the strongest predictor of obesity, with older adults having significantly higher odds of being overweight or obese.
2. Mental Health Predictors Among Adults in Selangor
This study assessed the prevalence of depression, anxiety, and stress (DAS) among adults in Selangor and their association with sociodemographic and lifestyle factors. Employment status, alcohol consumption, and sleep duration were significantly linked to mental health outcomes.
3. Eating Behaviors and Obesity in Children and Adolescents
This study aimed to determine the relationship between eating habits and BMI in children and adolescents. While no correlation was found between eating habits and BMI, the study noted that family history of obesity was significantly associated with BMI.
4. Depression and Social Support Among the Elderly in Selangor
This study screened for depression among elderly individuals in primary care settings, finding that race, education level, and social support were significant factors. Poor social support increased the likelihood of depression, emphasizing the need for early screening and intervention.
5. Help-Seeking Behavior in Urban Primary Care Clinics
This study analyzed the help-seeking patterns of patients with emotional distress or suicidal ideation. The findings showed that intimate partners and family members were the preferred sources of support, while a significant percentage of participants did not seek help at all.
6. Happiness and Life Satisfaction in Primary Care Patients
This study investigated the prevalence and predictors of happiness and life satisfaction among adults attending primary care clinics. Factors such as chronic diseases, physical activity, and smoking/vaping habits showed significant associations with life satisfaction levels.
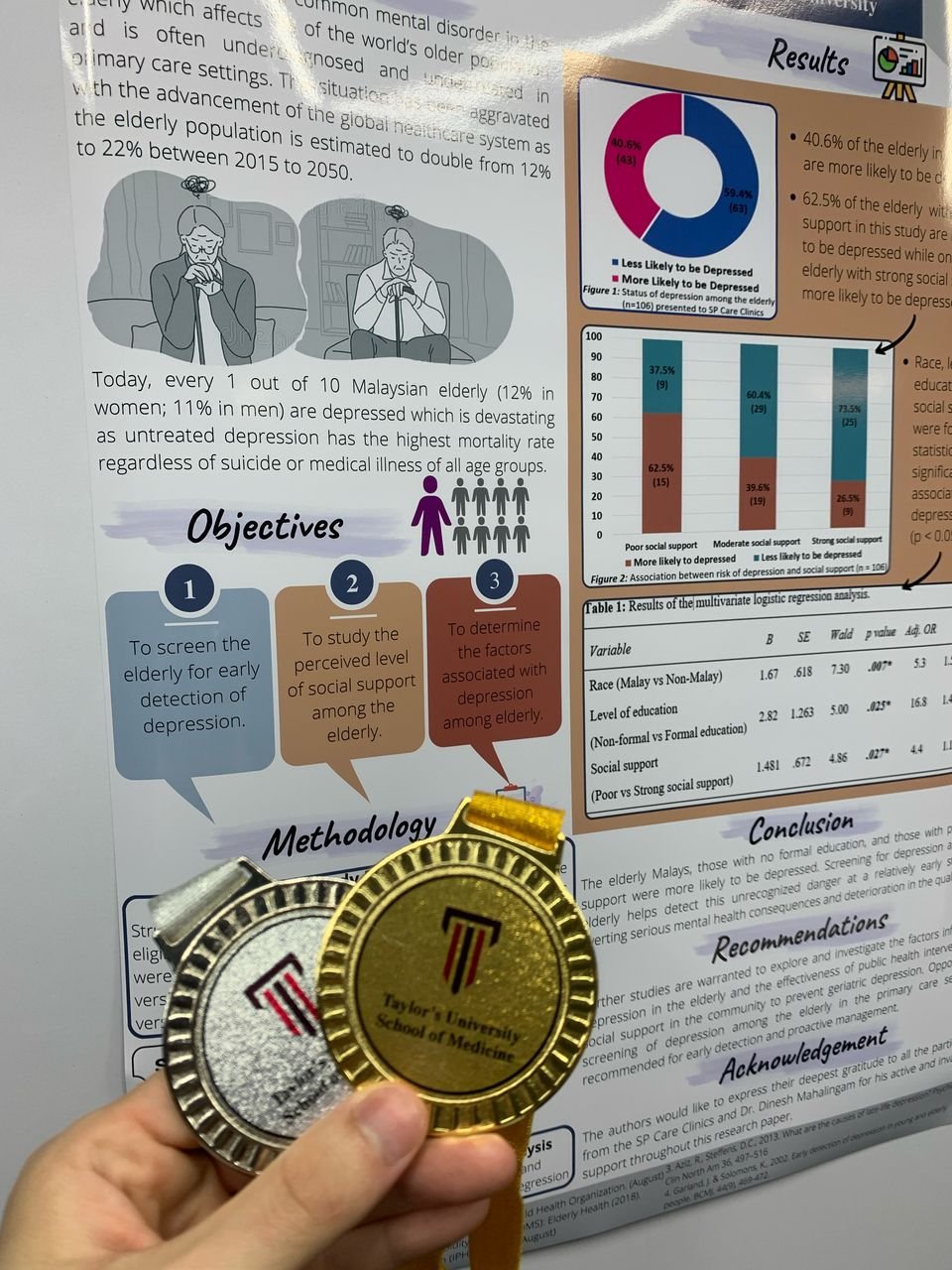
7. Screening for Depression in the Elderly
This study focused on early detection of depression among elderly individuals using validated screening tools. The results showed that Malays, those with no formal education, and individuals with poor social support were at higher risk of depression, highlighting the need for improved mental health interventions.

Batch 16
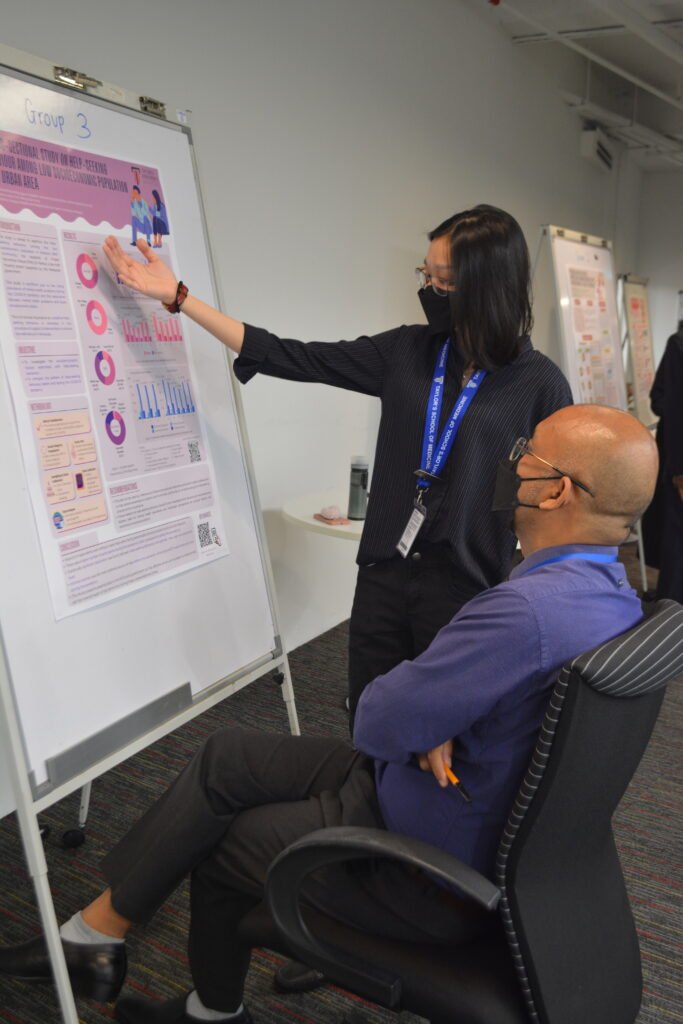
1. Help-Seeking Behavior Among Low Socioeconomic Populations
This study examined the factors influencing help-seeking behavior among Malaysia’s B40 community, particularly in PPR Sri Pantai, before and during the COVID-19 pandemic. The findings highlight the role of sociodemographic factors in accessing support for mental health and personal issues.
2. Happiness Index Among PPR Sri Pantai Residents During COVID-19
Researchers assessed the prevalence and predictors of happiness among low-income urban residents during the pandemic. The study explored how economic, social, and mental health factors influenced well-being.
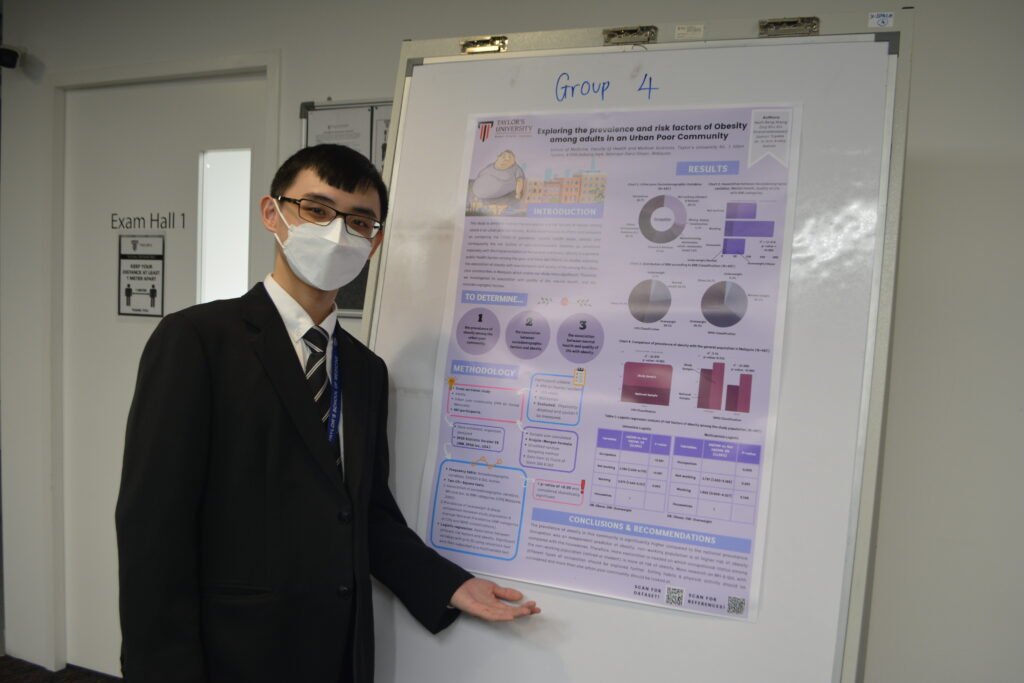
3. Obesity Risk Factors in an Urban Poor Community
This study analyzed the prevalence of obesity and its associated risk factors, including lifestyle habits, diet, and socioeconomic influences, among adults in a low-income urban community.
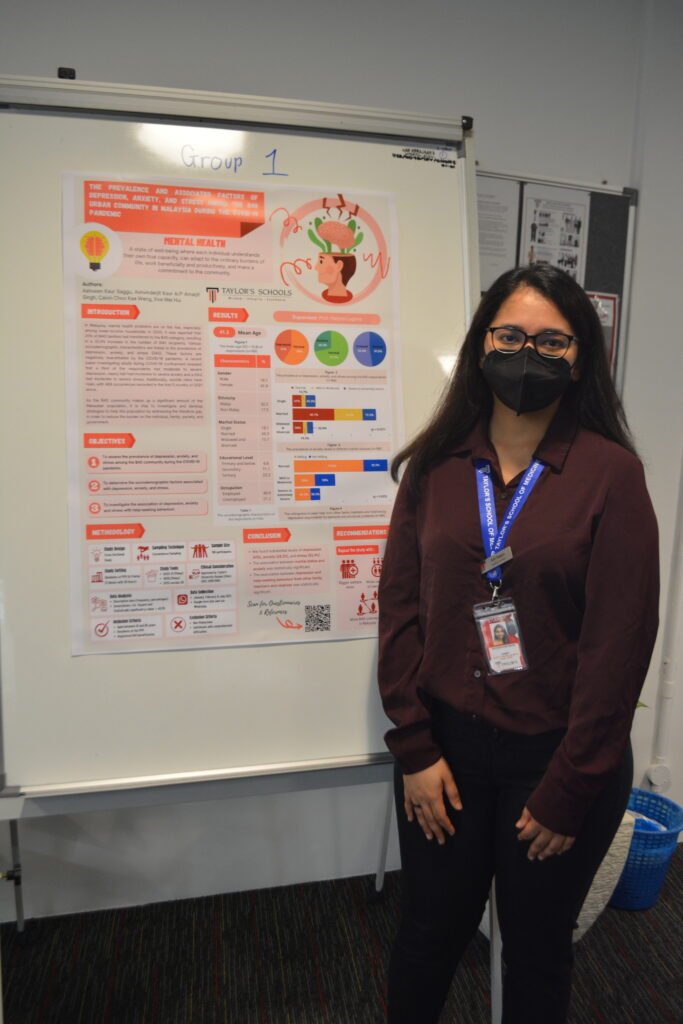
4. Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Among B40 Urban Residents
Investigating mental health during COVID-19, this study identified factors contributing to depression, anxiety, and stress among low-income individuals, emphasizing the pandemic’s psychological impact.
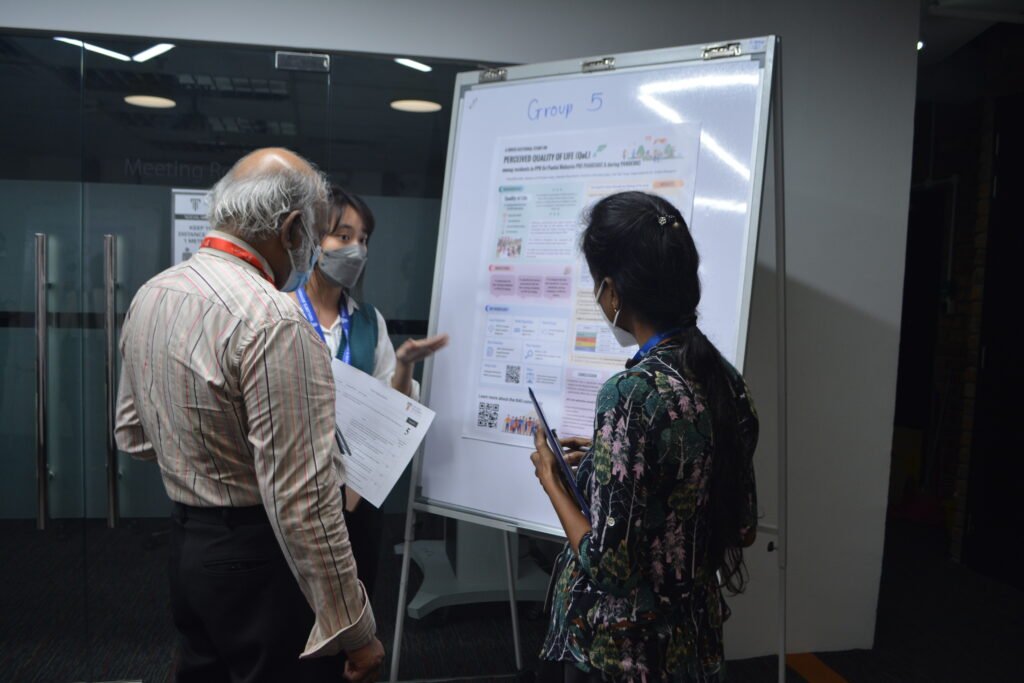
5. Quality of Life (QoL) in PPR Sri Pantai Pre- and Post-Pandemic
This study compared the perceived quality of life among residents before and during COVID-19, examining how financial, social, and environmental changes affected their well-being.
6. Hygiene Knowledge and Disease Transmission Among Primary School Children
Using the e-Bug tool, this community-based study assessed primary school children’s understanding of hygiene and disease prevention, highlighting areas for public health intervention.
7. Quality of Life and Its Correlation with Depression, Anxiety, and Stress
This study explored how different domains of quality of life are linked to mental health issues among adults in a B40 community, emphasizing the need for targeted interventions.









































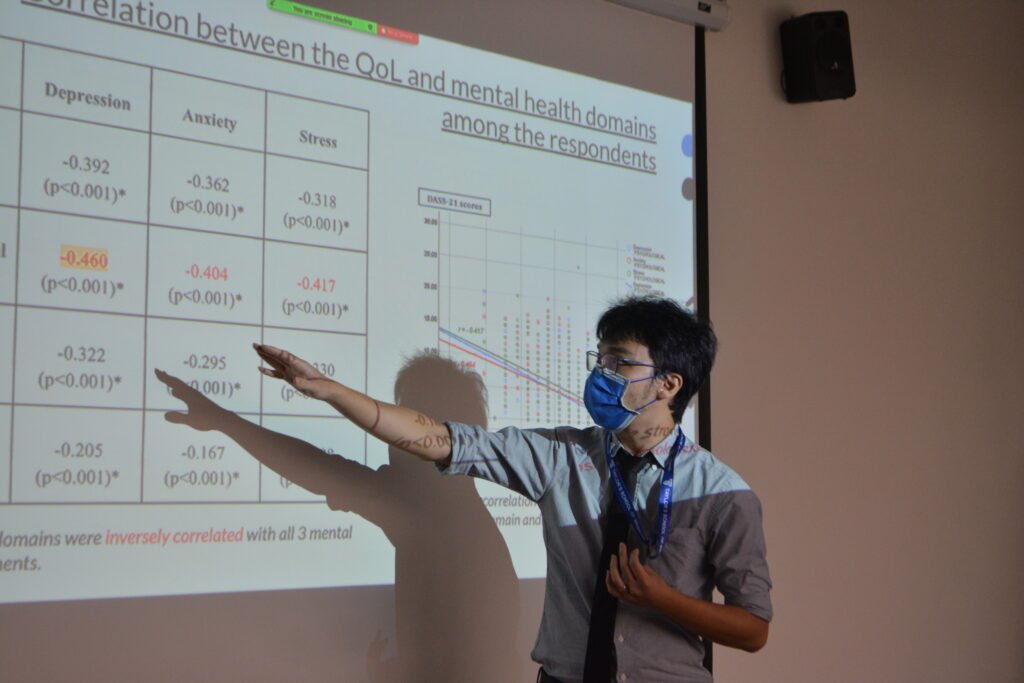









































Batch 15
1. Help-Seeking Behavior Among Low Socioeconomic Populations
Similar to Batch 16, this study focused on the factors influencing help-seeking behavior among the urban poor, particularly during the pandemic.
2. Happiness and Quality of Life in a Malaysian B40 Urban Community
Examining the link between happiness and perceived quality of life, this study highlighted how economic and social challenges affected well-being during the COVID-19 lockdown.
3. Effectiveness of the e-Bug Program
This study assessed the impact of the e-Bug educational program on improving hygiene awareness and disease prevention among school children.
4. Mental Health and Obesity Risk Factors in Urban Poor Communities
Investigating the relationship between mental health issues and obesity, this study explored how stress, lifestyle, and socioeconomic conditions contributed to weight gain during the pandemic.
5. Happiness Levels Among PPR Sri Pantai Residents
This research focused on the psychological well-being of low-income residents, identifying key determinants of happiness in an urban poor community.
6. Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Among B40 Residents in Kuala Lumpur
Conducted in the midst of COVID-19, this study analyzed the prevalence of mental health disorders and their associated sociodemographic risk factors.
7. Quality of Life Among Low-Income Residents During Malaysia’s MCO
Exploring the effects of lockdown restrictions on daily life, this study evaluated how movement control orders (MCO) impacted the quality of life in the B40 community.